Содержание
Elasticsearch can be installed on Windows using the .zip package. This comes with a elasticsearch-service.bat command which will setup Elasticsearch to run as a service.
The latest stable version of Elasticsearch can be found on the Download Elasticsearch page. Other versions can be found on the Past Releases page.
Elasticsearch requires Java 8 or later. Use the official Oracle distribution or an open-source distribution such as OpenJDK.
Download and install the .zip package
Unzip it with your favourite unzip tool. This will create a folder called elasticsearch-5.3.3 , which we will refer to as %ES_HOME% . In a terminal window, cd to the %ES_HOME% directory, for instance:
Running Elasticsearch from the command line
Elasticsearch can be started from the command line as follows:
By default, Elasticsearch runs in the foreground, prints its logs to STDOUT , and can be stopped by pressing Ctrl-C .
Configuring Elasticsearch on the command line
Elasticsearch loads its configuration from the %ES_HOME%configelasticsearch.yml file by default. The format of this config file is explained in Configuring Elasticsearch.
Any settings that can be specified in the config file can also be specified on the command line, using the -E syntax as follows:
Values that contain spaces must be surrounded with quotes. For instance -Epath.logs="C:My Logslogs" .
Typically, any cluster-w >cluster.name ) should be added to the elasticsearch.yml config file, while any node-specific settings such as node.name could be specified on the command line.
Checking that Elasticsearch is running
You can test that your Elasticsearch node is running by sending an HTTP request to port 9200 on localhost :
which should give you a response something like this:
Installing Elasticsearch as a Service on Windows
Elasticsearch can be installed as a service to run in the background or start automatically at boot time without any user interaction. This can be achieved through the elasticsearch-service.bat script in the bin folder which allows one to install, remove, manage or configure the service and potentially start and stop the service, all from the command-line.
The script requires one parameter (the command to execute) followed by an optional one indicating the service id (useful when installing multiple Elasticsearch services).
The commands available are:
Install Elasticsearch as a service
Remove the installed Elasticsearch service (and stop the service if started)
Start the Elasticsearch service (if installed)
Stop the Elasticsearch service (if started)
Start a GUI for managing the installed service
Based on the architecture of the available JDK/JRE (set through JAVA_HOME ), the appropriate 64-bit(x64) or 32-bit(x86) service will be installed. This information is made available during install:
While a JRE can be used for the Elasticsearch service, due to its use of a client VM (as opposed to a server JVM which offers better performance for long-running applications) its usage is discouraged and a warning will be issued.
The system environment variable JAVA_HOME should be set to the path to the JDK installation that you want the service to use. If you upgrade the JDK, you are not required to the reinstall the service but you must set the value of the system environment variable JAVA_HOME to the path to the new JDK installation. However, upgrading across JVM types (e.g. JRE versus SE) is not supported, and does require the service to be reinstalled.
Customizing service settings
The Elasticsearch service can be configured prior to installation by setting the following environment variables (either using the set command from the command line, or through the System Properties->Environment Variables GUI).
A unique >elasticsearch-service-x86 (on 32-bit Windows) or elasticsearch-service-x64 (on 64-bit Windows).
The user to run as, defaults to the local system account.
The password for the user specified in %SERVICE_USERNAME% .
The name of the service. Defaults to Elasticsearch %SERVICE_ID% .
The description of the service. Defaults to Elasticsearch Windows Service — https://elastic.co .
The installation directory of the desired JVM to run the service under.
Log directory, defaults to %ES_HOME%logs .
Data directory, defaults to %ES_HOME%data .
Configuration file directory (which needs to include elasticsearch.yml and log4j2.properties files), defaults to %ES_HOME%conf .
Any additional JVM system properties you may want to apply.
Startup mode for the service. Can be either auto or manual (default).
The timeout in seconds that procrun waits for service to exit gracefully. Defaults to 0 .
At its core, elasticsearch-service.bat relies on Apache Commons Daemon project to install the service. Environment variables set prior to the service installation are copied and will be used during the service lifecycle. This means any changes made to them after the installation will not be picked up unless the service is reinstalled.
On Windows, the heap size can be configured as for any other Elasticsearch installation when running Elasticsearch from the command line, or when installing Elasticsearch as a service for the first time. To adjust the heap size for an already installed service, use the service manager: binelasticsearch-service.bat manager .
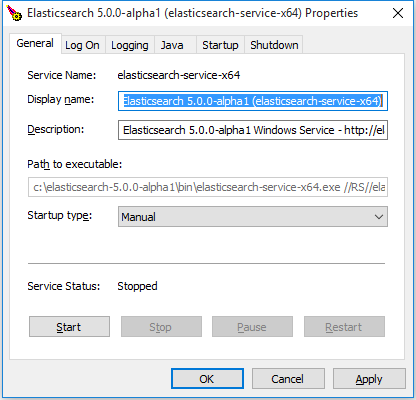
Most changes (like JVM settings) made through the manager GUI will require a restart of the service in order to take affect.
Directory layout of .zip archive
The .zip package is entirely self-contained. All files and directories are, by default, contained within %ES_HOME% — the directory created when unpacking the archive.
This is very convenient because you don’t have to create any directories to start using Elasticsearch, and uninstalling Elasticsearch is as easy as removing the %ES_HOME% directory. However, it is advisable to change the default locations of the config directory, the data directory, and the logs directory so that you do not delete important data later on.
| Type | Description | Default Location | Setting |
|---|---|---|---|